5.8 KiB
Gitea - Self Hosted GitHub
Before starting, make sure you have:
- Caddy web server installed (see Caddy guide)
- Docker and Docker Compose installed on your VPS
If you don't have docker installed, check the installation guide and install the docker engine.
Important: Add yourself to the docker group, so that you don't need to use sudo to run docker commands.
sudo usermod -aG docker new_user
Installation
We'll run Gitea using Docker (just a personal preference). Reference: installation guide
1. Set Up Docker Compose
Create a directory for Gitea
mkdir -p ~/gitea
cd ~/gitea
Create a docker-compose.yaml file inside the gitea directory
cd ~/gitea
touch docker-compose.yaml
Copy the content of docker-compose.yaml file to newly created docker-compose.yaml file.
2. Reverse Proxy Setup
To make Gitea accessible outside the server, we need to set up a subdomain for Gitea at https://git.domain.com and set up a reverse proxy with Caddy.
Create an A Record in your domain's DNS settings
- Name:
git(forgit.domain.com) - Value: Server's IP address
Create a reverse proxy for the git.domain.com domain in Caddy's config directory:
sudo vim /etc/caddy/conf.d/gitea.Caddyfile
Copy the content from gitea.Caddyfile.
After creating the config file, reload Caddy
sudo systemctl reload caddy
Change the GITEA__server__ROOT_URL environment variable inside the docker-compose file to the git subdomain.
Start the Gitea Docker Container
docker compose up -d
Gitea is now running on port 3000 and will show an installation wizard.
Installation Setup
Fill out the the details in installation wizard
Database: SQLite (just to keep it simple)
Site Title: A cool name or just use the default "Gitea"
Repository Root Path: Keep the default /data/git/repositories
Server Domain: Gitea domain git.domain.com
SSH Port: 2222
HTTP Port: Keep the default 3000 or just use any available port
Gitea Base URL: https://git.domain.com
Server Settings: Enable Local Mode and disable Self Registration if installing for personal use.
After this, just click on the Install Gitea button and your Gitea is ready to use!
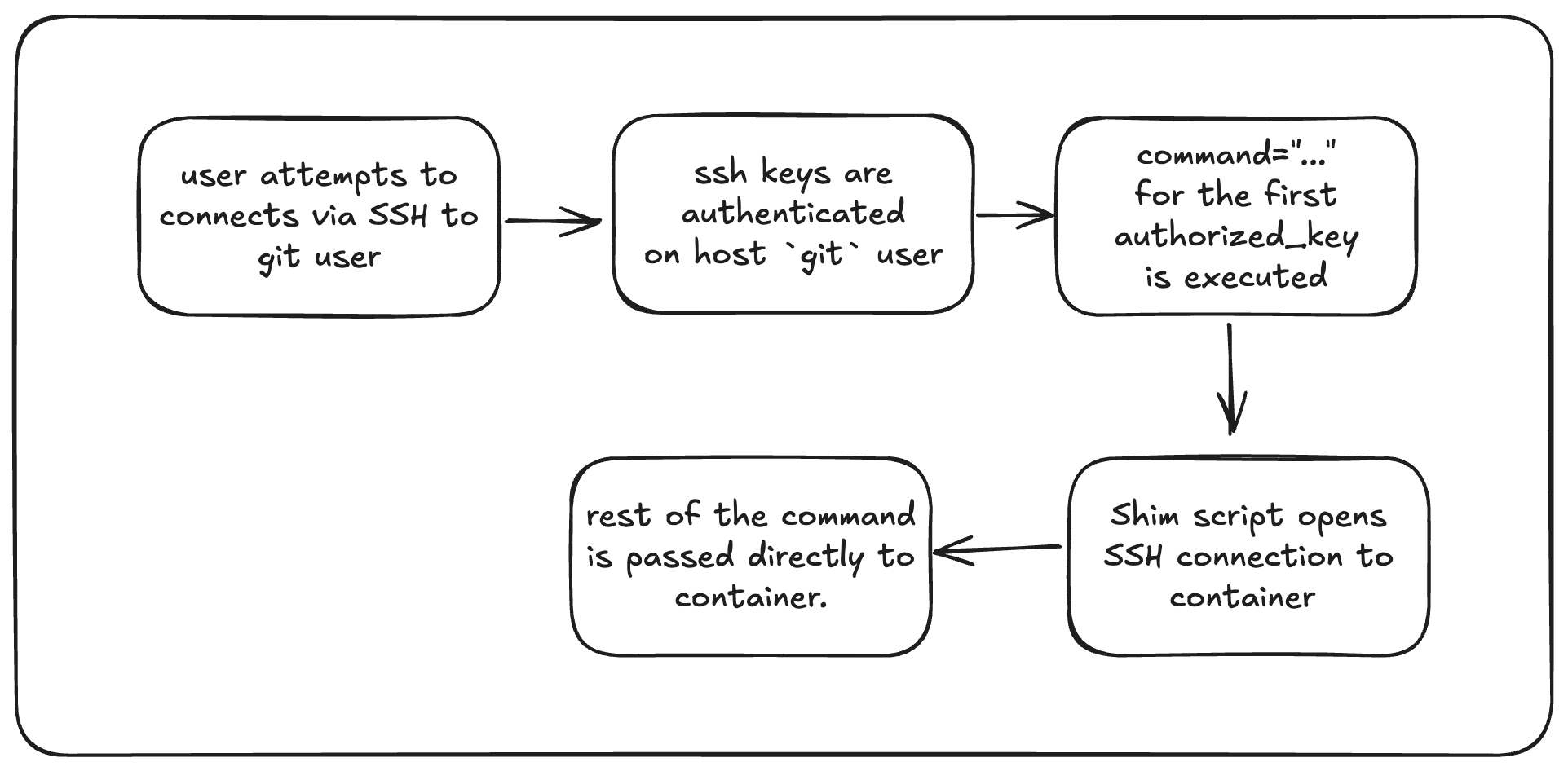
Enable SSH
Since Gitea is running inside a Docker container, we cannot directly access git via SSH. To achieve this we need to forward SSH connections from the host to the container.
To make this happen Gitea keys are prefixed with command = .... which executes the shim script (that we will create).
This script upon execution authenticates the host git user to docker container and passes the control to container.
Reference: Official Gitea Documentation
1. Create the git User on the Host
We'll create a special user called git.
When someone connects via SSH for Git operations, git user receives the connection and forwards it to the Gitea container.
sudo useradd -mr -s /bin/bash git
-m- Creates the user's home directory (/home/git)-r- Creates a system user (typically UID below 1000)-s /bin/bash- Sets bash as the login shell
Check the user id and group id of the user created
id git
# You should see something like
# uid=101(git) gid=101(git) groups=101(git)
2. Update Docker Compose Configuration
To make the forwarding work, the SSH port of the container (22) needs to be mapped to the host port 2222.
ports:
- "127.0.0.1:3000:3000"
- "127.0.0.1:2222:22"
Mount /home/git/.ssh directory to the container.
This is to ensure authorized_keys file is shared between the host and container.
volumes:
- gitea-data:/data
- /home/git/.ssh/:/data/git/.ssh # Share SSH keys between host and container
This will ensure that any ssh key added to gitea is also added to host's authorized_keys file.
Also update USER_UID and USER_GID environment variables to match the git user you just created.
This ensures file permissions work correctly.
environment:
- GITEA__server__ROOT_URL=https://git.domain.com/
- USER_UID=101
- USER_GID=101
3. Generate SSH Keys on Host
The git user on your server needs to connect to the Gitea container to perform git operations. Generate an SSH key that allows this connection.
sudo -u git ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -f /home/git/.ssh/gitea_key -N ""
This creates two files:
/home/git/.ssh/gitea_key- Private key (keep this secret!)/home/git/.ssh/gitea_key.pub- Public key
Also add the public key to authorized_keys. This allows the git user to SSH into the container.
sudo -u git cat /home/git/.ssh/gitea_key.pub | sudo -u git tee -a /home/git/.ssh/authorized_keys
sudo -u git chmod 600 /home/git/.ssh/authorized_keys
4. Configure SSH Shim Script
Now we'll create a script that intercepts SSH connections meant for Gitea and forwards them to the container.
cat <<"EOF" | sudo tee /usr/local/bin/gitea
#!/bin/sh
ssh -p 2222 -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no git@127.0.0.1 "SSH_ORIGINAL_COMMAND=\"$SSH_ORIGINAL_COMMAND\" $0 $@"
EOF
# make this script executable
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/gitea
After all the changes, restart the Gitea container
docker compose restart
5. Test SSH Access
Now users can add their SSH public keys to their Gitea accounts and use Git over SSH. It should work perfectly fine!
Try cloning a repository
git clone git@git.domain.com:username/repo.git